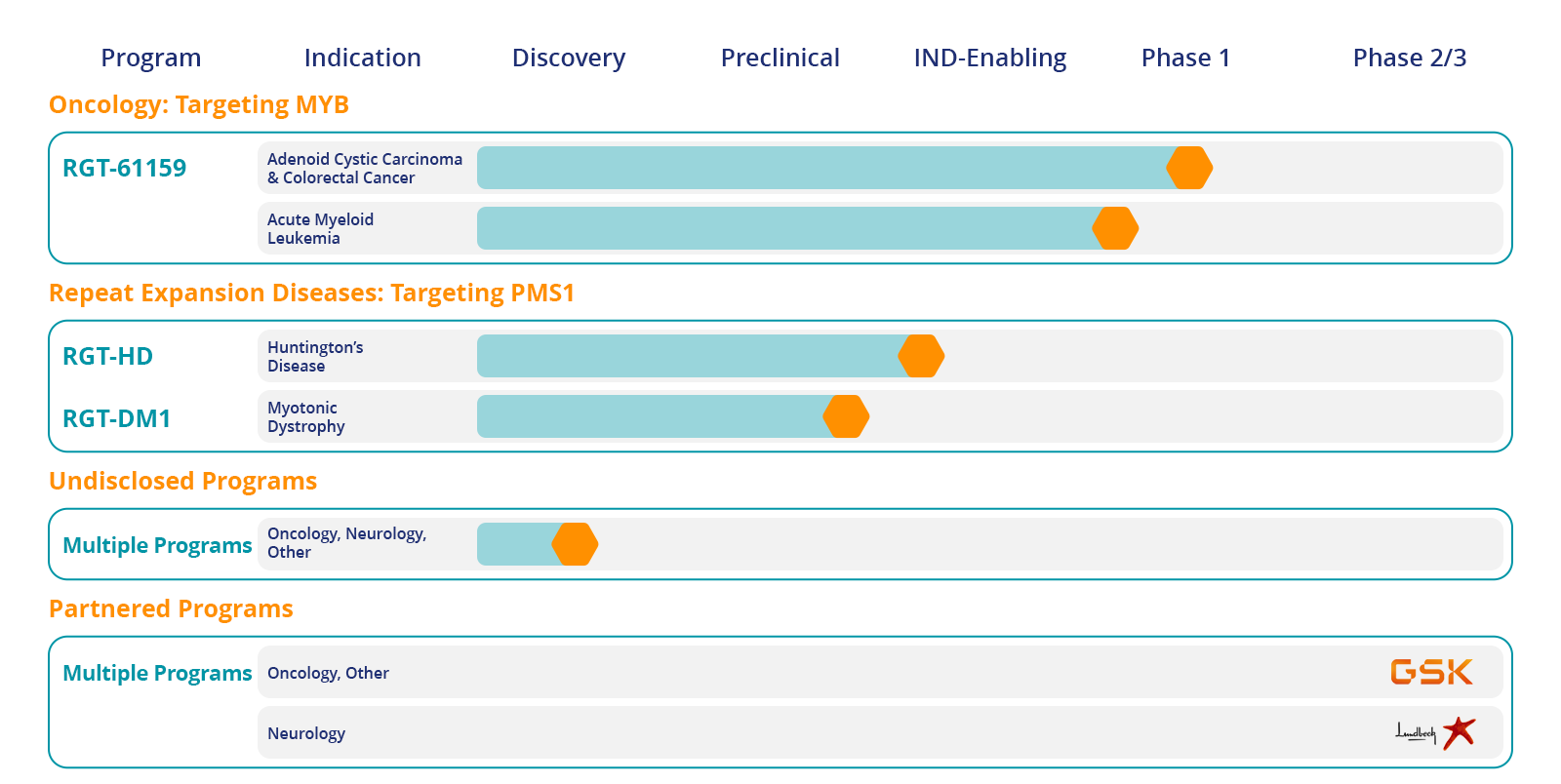
Our Pipeline
Our Priority Development Pipeline
Oncology
MYB - A Key Oncogenic Driver in Solid and Blood Tumors
As a master regulator of cell proliferation and differentiation, MYB’s aberrant expression has been implicated in multiple forms of human cancer, including adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC), acute myeloid leukemias (AML), Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS), T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias (T-ALL), colorectal cancer (CRC), small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and breast cancer.
RGT-61159
RGT-61159 is an orally available small molecule specifically designed to modulate the RNA splicing of the transcription factor MYB, effectively inhibiting the production of oncogenic MYB protein. By targeting MYB, RGT-61159 has the potential to suppress proliferation or induce cell death in cancer cells that overexpress MYB. RGT-61159 is currently being studied in a P1a/b trial for ACC and CRC. For more information, see our Clinical Trials.
CNS Disorders
Repeat Expansion Diseases (REDs)
These progressive diseases include more than thirty genetic disorders, including Huntington's disease (HD) and myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) characterized by the abnormal expansion of repeat sequences within an affected gene inherited at birth (e.g., 36-50 CAG repeats in HTT gene in HD). These inherited abnormal repeat sequences continue to expand through the lifetime of these patients through a process called somatic repeat expansion. When the repeats expand beyond a certain size threshold (>150 CAGs for HD), expression of the gene containing the abnormal repeats leads to the production of defective and toxic RNA or protein which has damaging effects in tissues.
Repeat expansion occurs when the mismatch repair (MMR) pathway mistakenly adds nucleotides in repetitive DNA sequences. This happens because the MMR system misinterprets unusual DNA structures that can form during DNA replication or transcription, leading to the expansion of the repeat region. Rgenta's novel approach to REDs targets a key component of the MMR, PMS1, and is designed to stop somatic repeat expansion, prevent repeats from expanding beyond the toxic threshold, and stall disease progression. In contrast, other therapeutic approaches are designed to reduce the expression of toxic RNA or protein after it is produced and the damage is already done.
PMS1
PMS1, a component of the mismatch repair (MMR) pathway, is a human genetics validated target required for continuous somatic expansion of repeats in REDs. Rgenta has designed a small molecule targeting PMS1 RNA which reduces its expression and leads to reduction in PMS1 protein levels and the halting of repeat expansion.
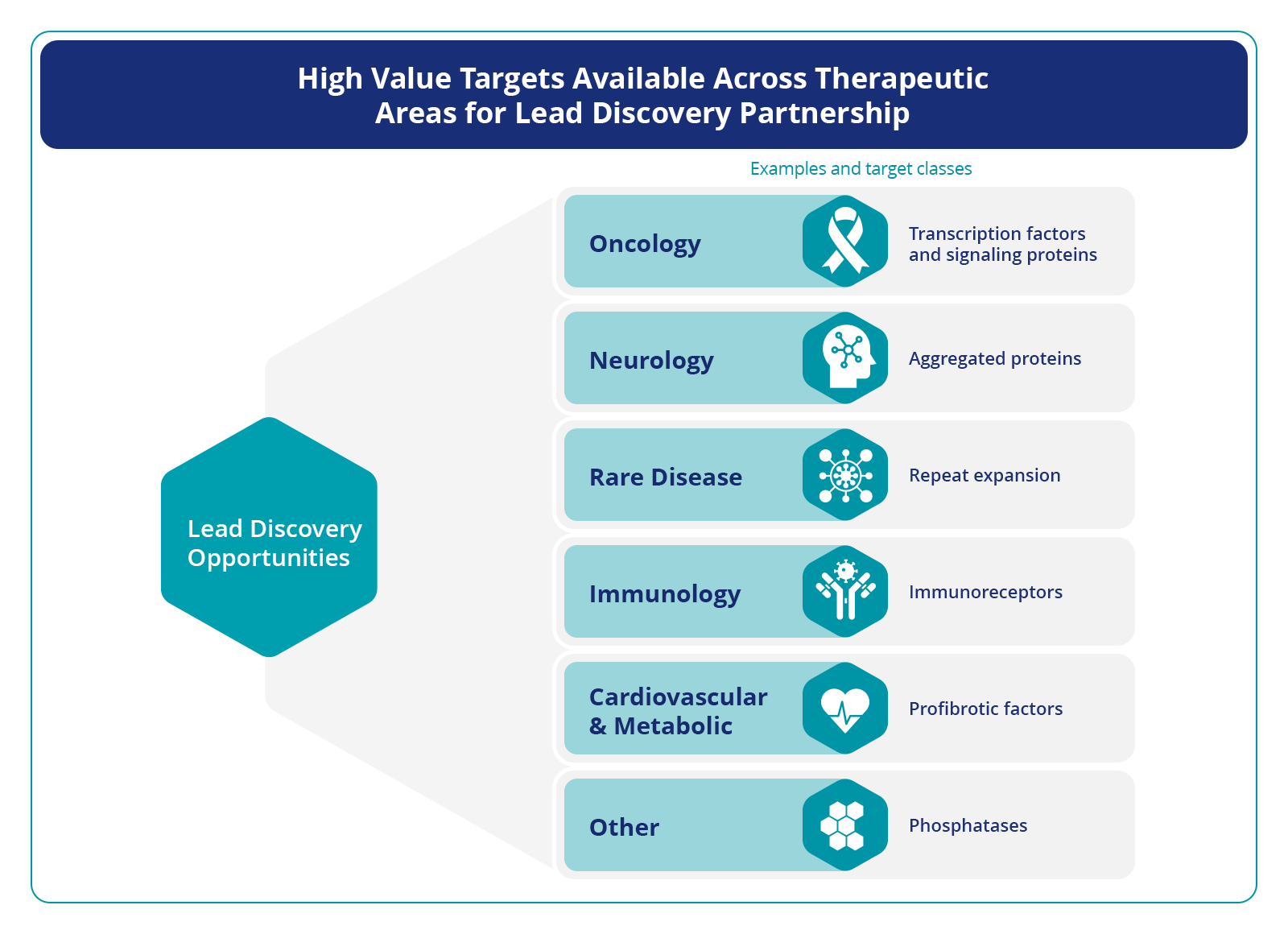
Broad Potential Opportunities in Multiple Therapeutic Areas
We are focused on oncology and CNS disorders, however we believe that Rgenta’s small molecule RNA-targeting approach has broad applications across multiple high value therapeutic areas.
Contact us at info@rgentatx.com to learn more about Rgenta’s programs.
